Medical billing and coding professionals are the unsung heroes of healthcare administration. These detail-oriented individuals ensure that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for their services by translating complex medical procedures and diagnoses into standardized codes. Without their crucial work, the financial backbone of healthcare systems would crumble. If you’re considering a career in this growing field, understanding the potential Medical Billing Coding Career Salary is a key factor.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), medical billers and coders are categorized under medical records specialists. This broader category highlights the important role these professionals play in managing health information. The latest BLS data indicates a median annual salary of $48,780 for medical records specialists nationwide. This figure serves as a solid starting point as you explore your earning potential in this vital healthcare career.
[Image of a data table showing national salary percentiles for medical records specialists, derived from the original article’s national data table.]
Alt text: National salary data for medical records specialists in the United States, including median, 10th, 25th, 75th, and 90th percentile annual earnings, and projected job growth.
This national median represents the midpoint of salaries across the country. However, it’s important to remember that your actual medical billing coding career salary can be influenced by a variety of factors. Let’s delve into some of these key elements that can impact your earning potential.
Medical Billing and Coding Salary: Location, Location, Location
Just like in real estate, location plays a significant role in determining your salary as a medical biller and coder. The cost of living, demand for healthcare services, and concentration of healthcare facilities all contribute to salary variations across different states and metropolitan areas.
As the original data from the BLS shows, there’s a considerable range in median salaries from state to state. For example, states on the West Coast and in the Northeast tend to offer higher median salaries compared to states in the Southeast. This difference is often attributed to a higher cost of living and greater demand for specialized healthcare services in these regions.
Here’s a look at the median medical billing and coding career salary across different states:
[Table of state salary data, same as original article’s state data table]
| State | Median Salary | Bottom 10% | Top 10% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $39,500 | $28,390 | $62,710 |
| Alaska | $55,280 | $43,230 | $81,530 |
| Arizona | $48,460 | $36,150 | $65,430 |
| Arkansas | $37,340 | $30,790 | $63,810 |
| California | $53,740 | $38,530 | $99,800 |
| Colorado | $55,660 | $40,010 | $82,980 |
| Connecticut | $61,300 | $37,420 | $86,440 |
| Delaware | $50,430 | $33,980 | $69,830 |
| District of Columbia | $61,320 | $47,570 | $108,310 |
| Florida | $44,210 | $31,520 | $80,270 |
| Georgia | $48,880 | $32,330 | $72,340 |
| Hawaii | $60,940 | $41,720 | $87,070 |
| Idaho | $49,650 | $36,480 | $69,060 |
| Illinois | $49,900 | $36,610 | $75,850 |
| Indiana | $46,410 | $34,370 | $65,360 |
| Iowa | $49,190 | $37,040 | $61,620 |
| Kansas | $46,750 | $33,990 | $67,970 |
| Kentucky | $44,770 | $31,760 | $64,810 |
| Louisiana | $48,810 | $31,110 | $74,300 |
| Maine | $45,630 | $37,190 | $68,640 |
| Maryland | $59,990 | $38,750 | $90,840 |
| Massachusetts | $52,330 | $39,170 | $83,840 |
| Michigan | $47,810 | $35,810 | $66,620 |
| Minnesota | $60,570 | $45,740 | $76,140 |
| Mississippi | $38,200 | $28,300 | $61,520 |
| Missouri | $50,920 | $34,450 | $76,660 |
| Montana | $46,830 | $37,200 | $61,560 |
| Nebraska | $46,440 | $34,490 | $66,800 |
| Nevada | $45,270 | $34,440 | $66,070 |
| New Hampshire | $47,960 | $36,200 | $67,100 |
| New Jersey | $58,520 | $40,900 | $91,480 |
| New Mexico | $45,240 | $34,140 | $67,440 |
| New York | $59,050 | $38,340 | $82,850 |
| North Carolina | $46,440 | $33,050 | $69,250 |
| North Dakota | $49,320 | $37,620 | $70,940 |
| Ohio | $48,010 | $35,430 | $72,580 |
| Oklahoma | $49,510 | $33,330 | $67,510 |
| Oregon | $54,080 | $39,110 | $83,250 |
| Pennsylvania | $46,160 | $36,590 | $63,720 |
| Rhode Island | $53,920 | $39,000 | $78,530 |
| South Carolina | $51,310 | $35,260 | $72,340 |
| South Dakota | $49,950 | $34,080 | $74,240 |
| Tennessee | $49,340 | $35,040 | $78,760 |
| Texas | $44,180 | $31,090 | $68,510 |
| Utah | $49,750 | $35,230 | $90,770 |
| Vermont | $49,610 | $38,570 | $69,630 |
| Virginia | $50,600 | $37,170 | $77,700 |
| Washington | $58,580 | $41,130 | $86,880 |
| West Virginia | $41,680 | $29,520 | $64,100 |
| Wisconsin | $51,870 | $38,540 | $70,240 |
| Wyoming | $51,360 | $37,300 | $75,590 |

Beyond the state level, salaries can also vary significantly within metropolitan areas. Cities with higher concentrations of large hospital systems and specialized medical facilities often offer more competitive salaries. Consider these top-paying metropolitan areas for medical billing and coding professionals:
[Table of metro area salary data, same as original article’s metro area table]
| Metro Area | Median Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Vallejo-Fairfield, CA | $75,250 |
| San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA | $73,840 |
| Stockton-Lodi, CA | $73,830 |
| San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA | $72,170 |
| Corvallis, OR | $67,770 |
| Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA | $64,660 |
| Urban Honolulu, HI | $64,540 |
| Sacramento–Roseville–Arden-Arcade, CA | $64,410 |
| Hartford-West Hartford-East Hartford, CT | $64,200 |
| Norwich-New London-Westerly, CT-RI | $62,950 |
As you can see, California dominates the list of highest-paying metro areas, reinforcing the trend of higher salaries on the West Coast.
Experience, Education, and Certifications: Boosting Your Salary
While location sets the general salary landscape, your individual qualifications and career choices play a crucial role in determining your specific medical billing coding career salary. Experience, education, and professional certifications are key factors that employers consider when setting compensation.
Experience: Like most professions, entry-level positions in medical billing and coding will typically command a lower salary than roles requiring years of experience. As you gain expertise and a proven track record of accuracy and efficiency, your earning potential will naturally increase. Employers value experienced professionals who can navigate complex coding systems and billing processes with confidence.
Education: While some entry-level positions may only require a high school diploma or GED and on-the-job training, pursuing higher education can significantly enhance your career prospects and salary potential. An associate’s or bachelor’s degree in health information management, medical billing and coding, or a related field demonstrates a commitment to the profession and provides you with a more comprehensive understanding of healthcare administration. Furthermore, formal education can open doors to more advanced roles and leadership opportunities.
Certifications: Professional certifications are highly valued in the medical billing and coding field. Earning certifications like Certified Professional Coder (CPC) from the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) from the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) demonstrates your competency and expertise to potential employers.
Robyn Korn, MBA, RHIA, CPHQ, an adjunct instructor of medical coding at Purdue University Global, emphasizes the importance of certifications: “If you have coding credentials, that looks good on your resume. They show you have a knowledge base employers are looking for, making them more likely to consider you.” Beyond initial certifications, specializing in niche areas like ophthalmology or gastroenterology can further boost your earning potential due to the specialized knowledge required.
Work Setting and Pay Structure: More Salary Influencers
The type of healthcare setting where you work also influences your medical billing coding career salary. Different work environments have varying budget constraints and revenue streams, which can impact compensation levels.
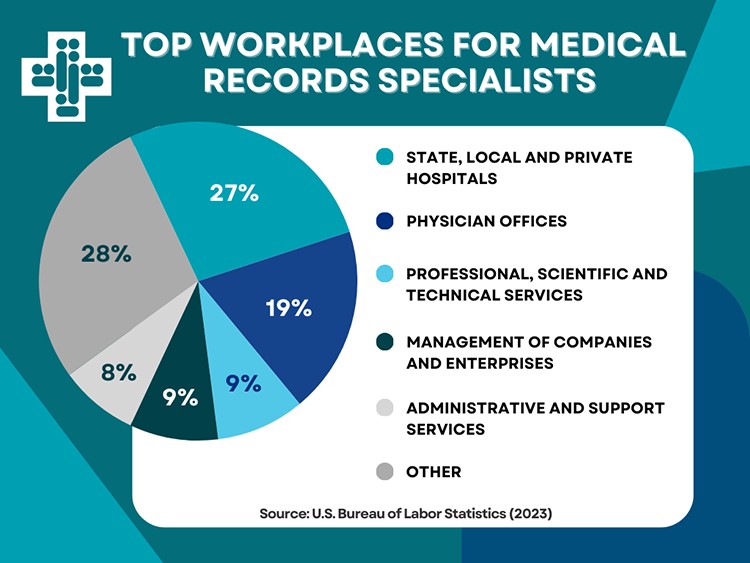
Generally, insurance agencies tend to offer the highest salaries for medical billers and coders. Hospitals, particularly large medical and surgical hospitals, typically fall in the mid-range for salaries. Physician’s offices and outpatient care centers may offer somewhat lower median salaries compared to hospitals and insurance companies.
[Image of a pie chart illustrating top workplaces for medical records specialists, same as original article’s workplace pie chart]
The way you are paid – your pay structure – also impacts your overall earnings. Medical billers and coders can be paid hourly, salaried, per case, or even on commission. Hourly pay is common, and overtime pay can increase earnings, particularly in busy healthcare settings. Salaried positions offer a fixed income, while per-case or commission-based pay structures can fluctuate depending on workload and efficiency.
Strategies to Maximize Your Medical Billing Coding Career Salary
While some factors influencing your salary are external, there are proactive steps you can take to increase your earning potential in a medical billing coding career.
- Invest in Education and Certifications: Continuously enhance your knowledge and skills by pursuing advanced certifications and degrees. Specializing in high-demand coding areas can also lead to higher pay.
- Gain Experience: Seek opportunities to work in diverse healthcare settings and gain experience with different coding systems and billing software.
- Network Professionally: Attend industry events and join professional organizations like AAPC and AHIMA to network with other professionals and learn about career advancement opportunities. As Robyn Korn advises, “When you network with other professionals in the field, you open yourself up to advance your career.”
- Consider Location Strategically: Research salary trends in different states and metropolitan areas and consider relocating to higher-paying regions if feasible.
- Negotiate Your Salary: Be prepared to negotiate your salary when accepting a new position. Research industry benchmarks and highlight your qualifications and experience to justify your desired compensation.
Promising Job Outlook for Medical Billing and Coding Professionals
Beyond salary considerations, the job outlook for medical billing and coding careers is exceptionally positive. The BLS projects an 8.7% job growth for medical records specialists through 2033, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
This strong job growth is driven by several factors, including an aging population requiring more healthcare services, advancements in medical technology, and the increasing complexity of healthcare regulations and insurance processes. As healthcare organizations expand to meet these growing needs, the demand for skilled medical billers and coders will continue to rise.
Resources for Your Medical Billing and Coding Career Journey
To further explore a career in medical billing and coding and enhance your professional development, consider these valuable resources:
- American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC): AAPC offers certifications, training, and networking opportunities specifically focused on medical coding for physician offices and clinics.
- American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA): AHIMA provides a broader range of resources for health information professionals, including certifications, education, and advocacy, covering various healthcare settings.
Written and reported by: Catherine Ryan Gregory Contributing writer
With professional insight from: Robyn Korn, MBA, RHIA, CPHQ Adjunct Instructor of Medical Coding, Purdue University Global
In conclusion, a medical billing coding career offers a stable and rewarding path in the healthcare industry with solid earning potential and excellent job security. By understanding the factors that influence medical billing coding career salary and proactively investing in your skills and career development, you can maximize your earning potential and build a successful and fulfilling career in this essential field.